Qualitizing Oral History Works-4
Characteristics of Interviewer
Mahya Hafezi
Translated by Ruhollah Golmoradi
2023-12-23
The Iranian Oral History Website has conducted short conversations with some experts and practitioners on the topic of how to improve oral history books or memoirs, the results of which will be presented to the readers in the form of short notes and in several parts.
Producing an oral history work is similar to make a building which has basic foundations. If these constituents are not provided correct, there would not be a desirable final product. An oral history work has two primary constituents: the first one is words that the interviewer states and the second is words that compiler collects. Most of any oral history work is about content that the interviewer expresses. In order to make useful what the interviewer says, the interviewer must extract the content elegantly and skillfully.
Therefore, the interviewer must have the characteristics to do a standard and successful work, which we will discuss further.
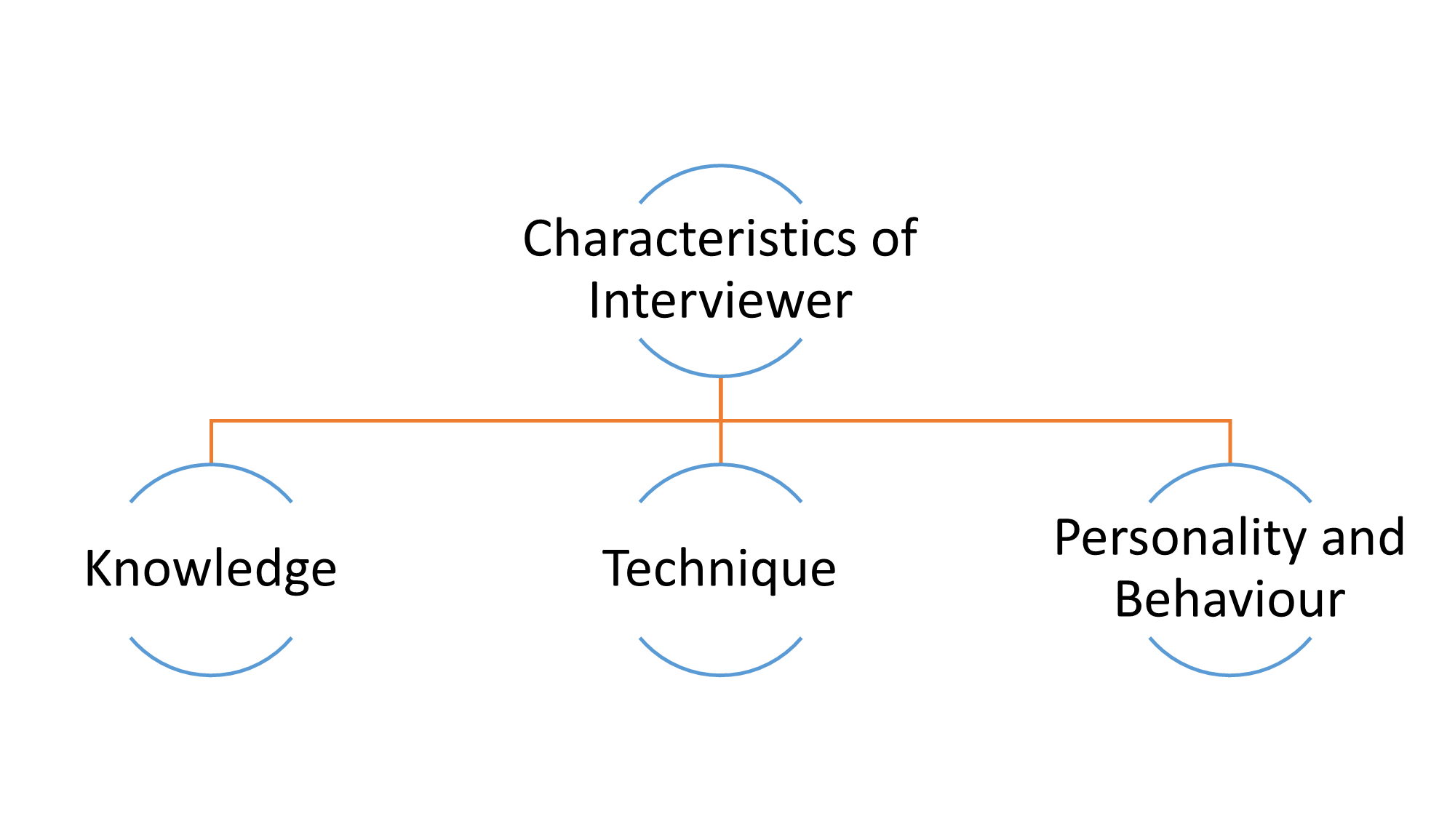
The characteristics of an interviewer include three general parts: “Knowledge”, “Technique”, and “Personality and Behavioral Characteristics.” That is, the interviewer must have the knowledge of interviewing, the technique of interviewing in oral history, and a normal personality and behavior characteristics in the society.
Knowledge
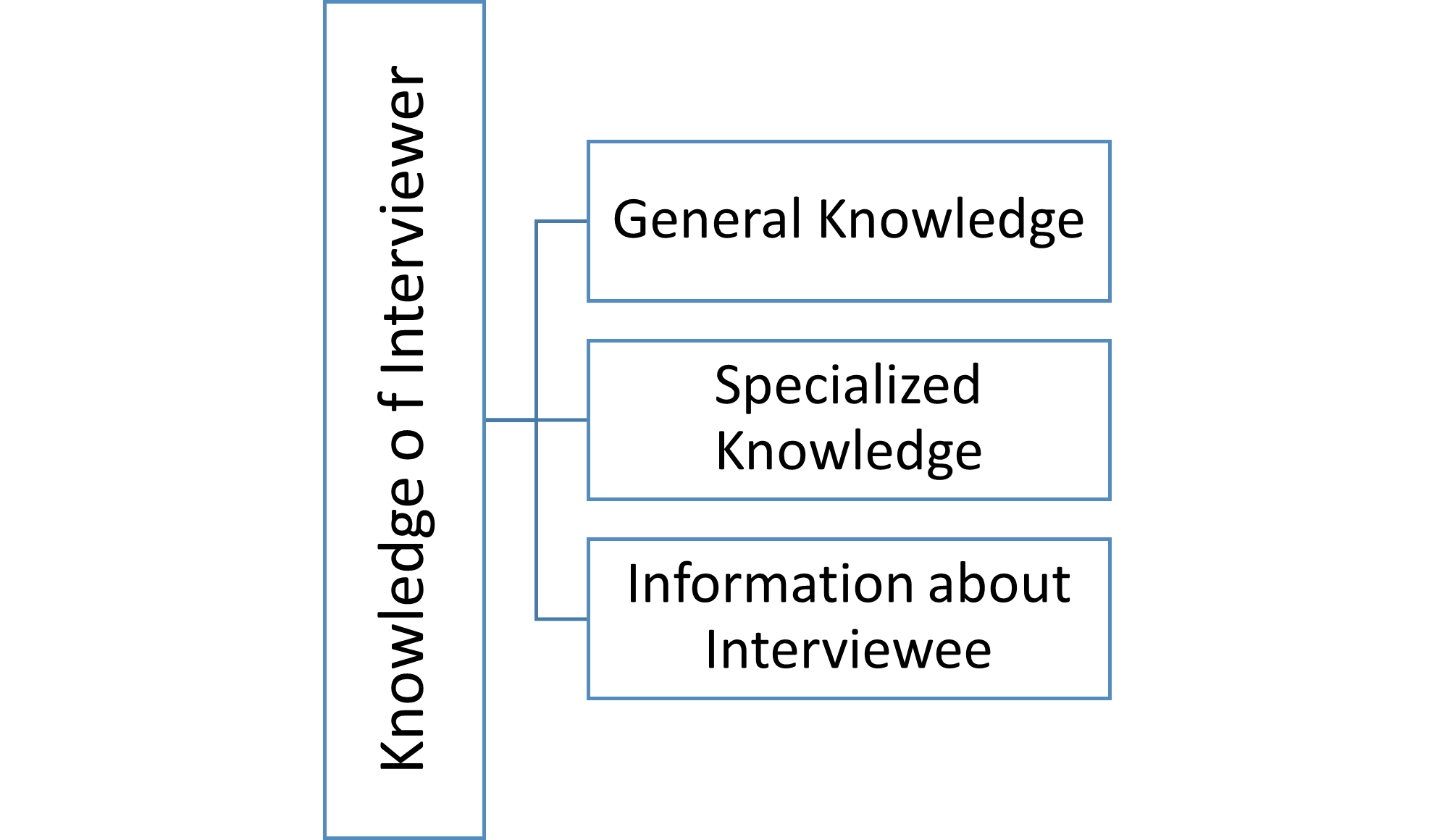
The interviewer's knowledge is classified into three parts: general knowledge, specialized knowledge, and information about the person being interviewed.
1- General Knowledge:
It is necessary for the interviewer to be familiar with general teachings, which is called general knowledge. These teachings are categorized in three parts: general information, IQ, and being knowledgeable of current events.
A) General Information
The basis of the interviewer's knowledge is to have the necessary and sufficient general information. A person with poor general knowledge cannot handle an interview well. If the interviewer does not have general knowledge, he/she has to constantly interrupt the interviewee to ask the most obvious questions.
If a person has a lot of historical and specialized information, but lacks general information, he/she will not be a successful interviewer. When the interviewee realizes that the person he/she is talking to is knowledgeable in different topics, he/she will enjoy the interview, and finally, it will be a good interview. It is important for the interviewee what general information the person sitting in front of him/her as the interviewer has.
B) IQ
Another characteristic related to the interviewer's general knowledge is to have a high IQ. He/she must be able to understand what the interviewee is saying. Also, he/she can correctly recognize the proper situations to ask different questions.
When it comes to intelligence, we face two terms, IQ and EQ. Intelligence quotient (IQ) is a measure of a person's reasoning ability, while emotional intelligence (EQ) is the ability to understand, evaluate, and control emotions. In fact, IQ usually refers to a person's intellectual ability. A person with a high IQ can use logic to solve problems.
C) Being Knowledgeable of Current Events
In order to communicate between the interviewer and the interviewee, it is necessary for the interviewer to have enough information about the events of the day. In order to start the interview process, it is necessary to have preliminary talks. There is no need these conversations to be related to the topic of the interview; For example, this conversation can be about the weather, new events that are happening, newspaper news, and so on. Talking about the events of the day can bring the interviewer and the interviewee closer together and provide a more intimate atmosphere for the interview.
2- Specialized Knowledge
The interviewer must have complete information about the subject of the interview. In order for the interviewer to be able to ask good questions and receive good answers, he/she must be superior to the interviewee in terms of specialized knowledge about the subject of the interview. In this case, the interviewer can prevent the interview session from going astray. The interviewer must be an oral historian, which means he has complete knowledge of subject of the interview.
3- Information about the Interviewee
The interviewer must fully identify the interviewee before conducting the interview. He/she must have collected all the subject's personal information that he/she may need during the interview. This information can include the interviewee's morals, family status, educational background, personal communications, and so on.
Number of Visits: 2236








The latest
- Practical Models for Simulating Texts in Distinguished, Signature Styles, Under the Use of AI Tools in Resistance Literature
- A Recollection by Ali Tahiri of a Military maneuver
- 100 Questions/17
- Third Regiment: Memoirs of an Iraqi Prisoner of War Doctor – 17
- Oral History News of December-January 2026
- Analyzing the Impact of Sacred Defense Memories on the New Generation: Usage in Transmitting Values
- The Sha‘baniyya Uprising as Narrated by Ali Tahiri
- 100 Questions/16
Most visited
- Oral History News of December-January 2026
- Third Regiment: Memoirs of an Iraqi Prisoner of War Doctor – 16
- The Sha‘baniyya Uprising as Narrated by Ali Tahiri
- Analyzing the Impact of Sacred Defense Memories on the New Generation: Usage in Transmitting Values
- 100 Questions/16
- Third Regiment: Memoirs of an Iraqi Prisoner of War Doctor – 17
- 100 Questions/17
- A Recollection by Ali Tahiri of a Military maneuver
Oral History of 40 Years
One of the main hypotheses regarding the reason for the growth and expansion of oral history in the modern era relates to the fact that oral history is the best tool for addressing lesser-known topics of contemporary history. Topics that, particularly because little information is available about them, have received less attention.Omissions in the Editing of Oral History
After the completion of interview sessions, the original recordings are archived, the interviews are transcribed, proofread, and re-listened to. If the material possesses the qualities required for publication in the form of an article or a book, the editing process must begin. In general, understanding a verbatim transcription of an interview is often not straightforward and requires editing so that it may be transformed into a fluent, well-documented text that is easy to comprehend.100 Questions/8
We asked several researchers and activists in the field of oral history to express their views on oral history questions. The names of each participant are listed at the beginning of their answers, and the text of all answers will be published on this portal by the end of the week. The goal of this project is to open new doors to an issue and promote scientific discussions in the field of oral history.The Role of Objects in Oral Narrative
Philosophers refer to anything that exists—or possesses the potential to exist—as an object. This concept may manifest in material forms, abstract notions, and even human emotions and lived experiences. In other words, an object encompasses a vast spectrum of beings and phenomena, each endowed with particular attributes and characteristics, and apprehensible in diverse modalities.

